Functional dysfunction 🟢🟡🔴⚫️

Or: crowning dysfunction queen!
In my last article I crowned context king.
But as I was doing the thinking for that article, I had this extremely irritating and insistent voice in my head saying “yeah, but you know that’s not how it actually works”. And even as I hit publish, I knew that the annoying voice was (very annoyingly) correct.
This isn’t how it actually works. At least not all the time.
But I deliberately focused on a single axis because you have to start somewhere.
A single dimension could never capture all the nuance of the world we work in; our systems are n-dimensional. So I deliberately ignored and stripped away other dimensions in order to simplify and focus on one element, namely, levels of process and standardisation within an organisation.
But just because you choose to ignore something doesn’t mean it goes away.
So this article is trying to address the missing part by adding a part two to this series on context. Because if context is king, dysfunction is queen.
Dysfunction?
Everyone has some experience with dysfunction, either at work, or in life. Dysfunction is a word that has a visceral connotation, you can sort of feel the word.
But what do we mean by dysfunction in a work context?
Workplace dysfunction is when the system isn’t working as it is “meant” to work. Roles are not in practice what their job-descriptions say they are. Decisions aren’t made at the forum the org structure says they are. The person with the power in the room isn’t the person with the title. Funding conversations happen offline and politics are everywhere.
It’s a matter of degree. A system can be a little dysfunctional, or a lot.
Introducting the dysfunction scale
As soon as I started talking, thinking, mulling, chatting about this concept, I imagined a dysfunction speedometer. I simply had to draw it! Introducing the Dysfunctiometer! 🍏🍋🌶️🏴☠️
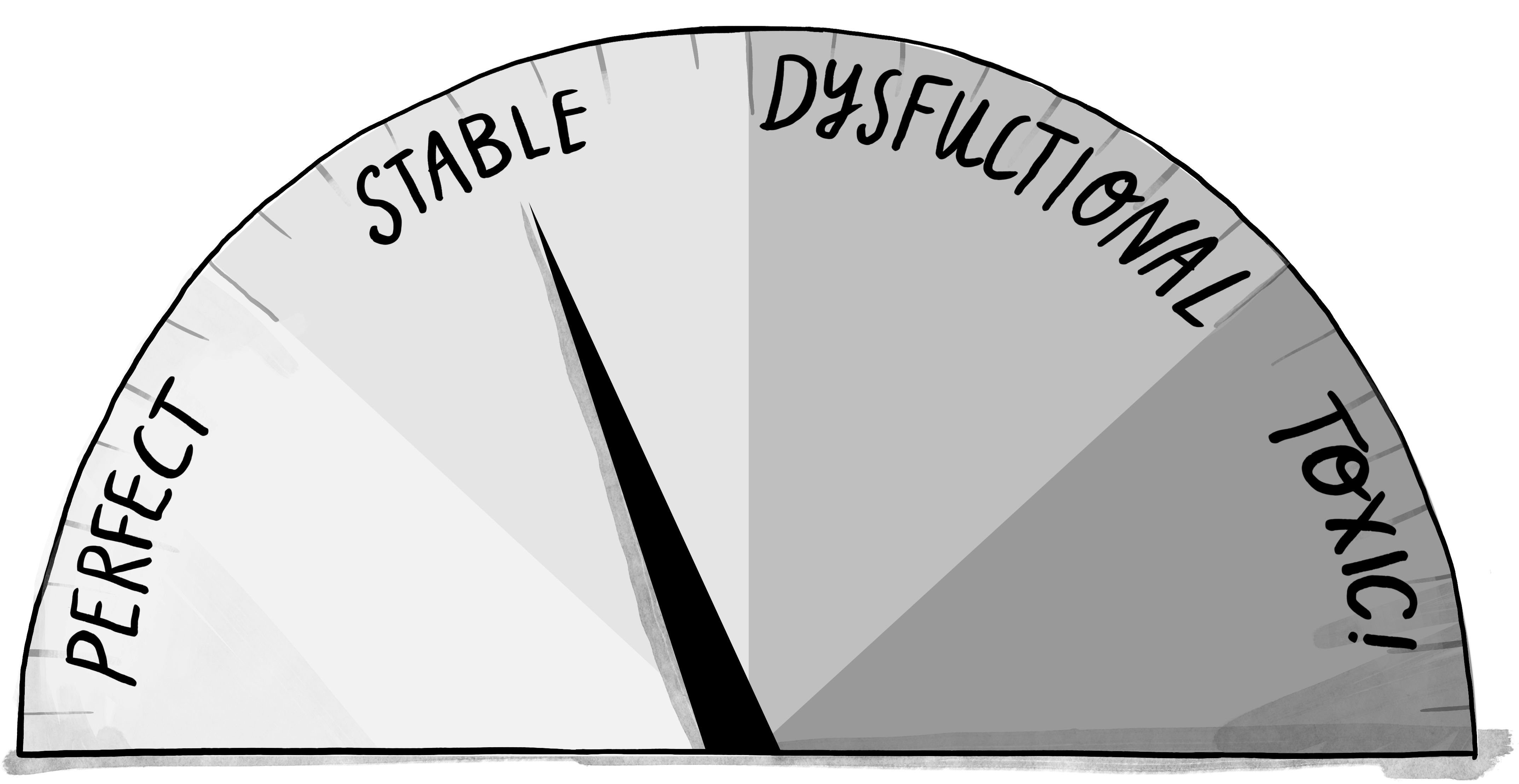
We all know that in a continuum the placement of boundaries is somewhat arbitrary, but for sake of simplicity, I’ve split the dysfunction scale into four different bands so we can talk about them.
Let’s start at the bottom where everything is happy, green, and dreamy …
🟢 A perfect system
Ah, the mystical perfect system! A Perfect system is lean and mean. People act entirely within their roles and they don’t have too much work (the dream!). Things are smooth and there’s no need for lots of layers of control.
In a Perfect system if someone has a question, they can simply contact the necessary person for an answer. Concerns are raised, and the system has the necessary feedback loops to course correct.
From what I’ve seen, perfect systems are rare, but I’ve certainly experienced elements of them in the wild, and I’ve definitely seen parts of a system that ran perfectly. Its really reassuring that smooth sailing is actually possible!
The very definition of dreamy!
But of course we are just at the very lowest levels of the Dysfunctionmeter… so let’s dial up a notch!
🟡 Stable systems
Stable systems have some dysfunction, but aren’t in-and-of-themselves dysfunctional! Stable systems have some characteristics that mean they can’t quite operate optimally if simply left alone.
Examples include:
- The tech is complicated and there are multiple teams working on the same codebase.
- The business is complex enough to require discussions across different areas to understand what is required.
- The system isn’t quite resourced in a way that enables smooth sailing. People have to step out of their core roles to keep things moving.
Stable systems are super common and they just need a bit of help!
Help can take many forms, but most commonly it includes adding facilitators, process, more specialised roles, and usually, more check-points to ensure we’re on track. And business analysts are (of course) one of the specialist roles that can help the flow.
With the right help, a stable system can function as well as a perfect system. And that’s typically what you’re trying to achieve – you’re attempting to counter the effects of the challenges on the flow of value. All systems are different, and selecting the right interventions is key to getting a good result.
For a Stable system, you’re just adding support to the existing system, not making changes to the system itself. It is imbalanced, not actually flawed!
And when a stable system starts to hum, and starts to work as well as a perfect system, you know you have your interventions spot on!
If you’ve been following along from last month’s article, here’s the overlap! In Context is King I posited that most business analysts operate in Established systems and that most advice is geared towards that environment. I believe it is also fair to claim that most business analyst advice is assuming a Stable system (in an established environment).
Things are slightly less easy to provide advice on as we dial up the dysfunction …
🔴 Dysfunctional systems
A dysfunctional system is a system that’s got significant enough challenges that simply adding some support won’t fix it.
A dysfunctional system requires intervention to the system itself in order to work effectively. With lots of effort, the system can work as well as a stable system, but can’t get to perfect without serious intervention!
One of the earliest signs of a dysfunctional system is that some or more of the team members regularly need to work late to keep things moving. Staying late – and that doing so is a necessity – is a sign that the system isn’t resourced correctly.
Incorrect resourcing is the lowest form of dysfunction.
Other, slightly more dysfunctional, examples include:
- Dependencies between teams are so significant that work is often held up waiting for other parts of the puzzle to be delivered.
- There aren’t clear accountabilities and responsibilities, so decisions keep getting re-litigated. The roadmap keeps changing.
- Key skills are missing from the team, so people are acting into roles that they don’t have the core competencies for.
- People are hesitant to talk openly about the issues.
- People are protective of their patch.
Where a stable system can be neutral (energy wise), a dysfunctional system is not. People burn out, are stressed, and work is just hard.
Another – somewhat surprising – way to tell that you’re in a dysfunctional system is the presence of heroes. 🦸♀️
We need to talk about the hero in the room ...
You know the person I’m talking about. Works late and single-handedly pulls together a plan to get you out of the mess. People talk breathlessly about how we couldn’t have done it without them. Everyone goes to them for the details. And their name gets thrown around as the fix for everything.
You might have even been a hero at one point (it was stressful, no?)
If there are heroes, there’s likely to also be villains. You know who I’m talking about!
Everyone knows they’re causing problems! They aren’t performing their role but there’s no performance management in sight. Their poor performance is openly acknowledged – at least behind their back. People are annoyed at the impact, and avoid dealing with them directly.
But this article isn’t about individuals; today we’re interested in the system, and what having heroes (and villains) tells you about the system.
It tells you that your system is broken enough to create them.
That hero is your system’s most likely point of failure. They are hiding the system weaknesses. They introduce artificial conditions into the system and make it harder for the real system issues to be recognised. And if you can’t get the issues acknowledged, good luck actually getting mandate to make the necessary changes.
When you think about it, you’ll notice that heroes – no matter how hard or well they work – never actually manage to fix things. And that’s because they’re just making things appear okay, however temporarily.
Villains do a similar thing but in an opposite way. They collect blame about what isn’t working, they become the target of people’s frustration. And because we all know it’s their fault people stop looking for the actual underlying root causes. It’s the system that enables poor performance, no one chooses to suck at their job …
In short, heros and villains are not good news.
Instead of heroics or simply attributing blame, a Dysfunctional system needs changes to the system itself in order to stabilise. Just working within the system won’t move the needle.
Without intervening at the system level, the system is likely to deteriorate further. And if it deteriorates too much you’ll end up with a toxic system …
⚫️ Toxic systems
The most dysfunctional systems are toxic.
A Toxic system has deteriorated to the point where interacting with the system isn’t good for anyone. Things are seriously wrong.
What the system delivers and its stated goals are wildly divergent. The system needs significant changes in order to get better. Think people leaving, major process changes, and likely a cultural reset. Examples include:
- There is visible tension between teams and departments over priorities and the work.
- Priorities appear to be more about what is good for people in power, and not the organisation itself. Politics abound.
- People are stressed and it isn’t uncommon for tempers to flare.
- No one wants to make decisions because of the potential for blame to be associated with actually committing to something.
- The team is chronically under resourced.
- There is significant pressure to report that everything is fine. Reality and reports diverge accordingly.
Which is all to say: the system is borked. Like really borked. It doesn’t matter how excellent you are at your job, unless you have serious mandate to pull the system apart, there is little you can actually do to help. At best you can keep it limping.
And even getting to a limp will likely take significant effort.
You should be asking yourself some hard questions about whether it is worth it. The reality is that unless you’re actually the CEO, or someone seriously powerful, toxic systems should be just avoided at all costs.
Yeah so, why does this matter?
But now that we’ve maxed out the dysfunctiometer, it’s time to step back and ask, what’s the point of this discussion?
The reason why dysfunction is such an important topic for business analysts is that if you really imagine an ideal and perfect system, one with absolutely zero dysfunction, business analysts wouldn’t be required.
No really. Think about it!
In a truly ideal world, in a perfect system, managers and decision makers have the skills and time to properly analyse situations, clarify their needs, identify options, and shape solutions. In that ideal world, they’d have time and relationships with a development team and would be able to work with them to deliver solutions that were fit for purpose!
In a perfect system, a business analyst isn’t required—because the system works perfectly!!
The truth is, we business analysts require some dysfunction in the system to exist in order to be helpful. The “dysfunction” could be minor …
Maybe the Product manager just doesn’t have the time for all the deep-dive analysis needed to make good decisions. Or it could be that there are just too many stakeholders involved for one person to manage all the relationships and information. Or the technical team prefers to focus on the solution and doesn’t want to take time away from the tools to get answers from SMEs.
The truth is, by the time we arrive on the scene, we already have some dysfunction in play.
And like the proverbial frog, it’s hard to tell when the water is getting too hot! 🐸
Temperature check 🌡️
Dysfunction is easy to identify in other people’s environments, but much harder to spot in our own.
There are lots of reasons for that, but much of it comes down to all the expectations we carry around! We should have found the cause. We should have delivered on time. We should have done that faster. We should have spent more time with our kids/friends/partner/cat. We should be better. We should get more done. We should, should, should.
And then we project those expectations onto our environment and then proceed to experience stress when reality and our expectations don’t line up (gosh it must have been that I misunderstood what was happening there, or I should have approached that differently.)
And if we aren’t projecting, we are normalising the dysfunction (aren’t all team meetings stressful?). Experience helps you identify abnormalities in the system.
Being able to see around the shoulds and objectively see how the system is working is a muscle you need to train. And if you’re having difficulty, sometimes it is easier to practice being objective with your previous work environments (it is amazing what a couple of years of separation can do for objectivity).
Knowing your environment is helpful to understanding how to help it.
But it is missing another key part of the equation …
What's your spice tolerance?
Knowing what environment you’re in is like knowing what the chilli pepper icons mean on hot sauce bottles. For that information to be useful you need to know what your own personal spice tolerance is.
If you are ordering dinner, do you avoid the spicy foods? Or do you like a bit of spice so order medium? Or do you like living dangerously and order the real spicy dish? 🌶️🌶️🌶️
Your preference is neither right or wrong, it just is. Everyone is different. What is fun for one person, might be boring to another. And what might be way too full on for someone, might feel like a genuinely fun challenge to another!
But it isn’t just preference, there’s a component of this that’s more comparable to having a tolerance level. There’s a certain level of spice that your body copes with, and a level that isn’t fun!
But unlike a spice tolerance level: Your tolerance is somewhat flexible
I love me a somewhat dysfunctional environment – I think navigating the complex system is deeply interesting.
But that statement comes with a huge unspoken caveat: I love a dysfunctional environment where I have the support to make a positive impact! Without support or mandate the dysfunction is just depressing because I can’t do anything about it! There is nothing worse than slaving away and knowing it’s not actually moving the needle.
The point is, there’s a ton of factors that can increase or decrease your tolerance: Having a mandate or a very supportive boss will increase your tolerance, but your home-life being a bit under pressure will decrease it.
So it’s not just knowing your preferences, but also keeping within your own personal tolerance levels. Or if you have to operate outside of your levels, being kind to yourself and making sure you are doing good self care (while you navigate your way to safer waters).
It’s hard to be anyone other than you, so you should do you well!
End notes!
Phew! I did not think it was going to be a long article when I started, and yet here I am some two and a half thousand words later! Turns out I have no idea how many words are in any single topic. 🤷♀️
I’ll stop adding to them now.
But I’ll leave you with a reminder that you have way more agency in your journey than you probably believe. And being able to accurately judge what you can and what you want to deal with is incredibly powerful part of that. 🙌
And some things to keep in mind:
- Your preferences are your own.
- You can only position yourself well if you know what “well” looks like for you!
- Some environments are never worth it.
Hey, tell me what you think!
Please do hit me up on LinkedIn or by email if you have any feedback! I’m always up for difficult questions, and always love nattering about business analysis!